AWS Mastery: 7 Ultimate Secrets to Dominate Cloud Computing
Welcome to the ultimate guide on AWS — where cloud innovation meets real-world power. Whether you’re a beginner or a pro, this deep dive reveals everything you need to know to harness Amazon Web Services like a true expert.
What Is AWS and Why It Dominates the Cloud World

Amazon Web Services, commonly known as AWS, is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform. Launched in 2006, AWS offers over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally, serving millions of customers — including startups, enterprises, and government organizations.
The Birth of AWS: A Game-Changer in Tech History
AWS wasn’t just another product launch — it was a revolution. Before AWS, companies had to invest heavily in physical servers, data centers, and IT infrastructure. Scaling was slow, expensive, and inefficient. AWS changed that by introducing on-demand, scalable computing power.
- AWS officially launched in 2006 with three core services: S3 (storage), EC2 (compute), and SQS (messaging).
- It was born out of Amazon’s internal need to scale its e-commerce platform efficiently.
- By opening its infrastructure to others, Amazon pioneered the modern cloud computing era.
“AWS didn’t just create a new market — it defined it.” — Forbes, 2020
How AWS Compares to Competitors Like Azure and Google Cloud
While Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are strong contenders, AWS holds the largest market share — approximately 32% as of 2024, according to Synergy Research Group.
- Market Leadership: AWS has been the market leader for over a decade, thanks to its early start and continuous innovation.
- Service Breadth: AWS offers more services than any other cloud provider — from AI and machine learning to IoT and serverless computing.
- Global Reach: With 33 geographic regions and 102 Availability Zones worldwide, AWS provides unmatched global coverage. Learn more about AWS global infrastructure.
Core AWS Services Every Developer Should Know
To master AWS, you must understand its foundational services. These are the building blocks of nearly every cloud architecture on the platform.
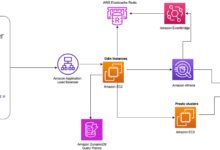
Amazon EC2: The Backbone of AWS Compute
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) allows users to rent virtual servers in the cloud. It’s one of the most widely used AWS services.
- Offers resizable compute capacity — scale up or down based on demand.
- Supports multiple instance types optimized for different workloads (e.g., memory-intensive, GPU-based).
- Integrates with Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing for high availability.
EC2 is ideal for hosting websites, running applications, and processing large datasets. It gives developers full control over their virtual machines while reducing the need for physical hardware.
Amazon S3: Scalable Cloud Storage for Everything
Simple Storage Service (S3) is AWS’s object storage solution, designed for storing and retrieving any amount of data at any time.
- Used for backup, archiving, big data analytics, and serving static website content.
- Offers 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability — meaning your data is extremely safe.
- Supports versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication.
S3 is the go-to storage service for companies like Netflix and Airbnb, which rely on it for media storage and content delivery. Explore Amazon S3 features.
Amazon RDS: Managed Relational Database Service
Relational Database Service (RDS) makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale relational databases in the cloud.
- Supports popular engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and Amazon Aurora.
- Automates time-consuming tasks like patching, backups, and failover.
- Enables read replicas for improved performance and disaster recovery.
RDS is perfect for applications requiring structured data storage without the overhead of database administration.
How AWS Powers Modern Businesses and Startups
From Fortune 500 companies to garage-based startups, AWS is the engine behind digital transformation. Its flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency make it the preferred choice for businesses of all sizes.
Startups Accelerate Growth with AWS
For startups, capital efficiency and speed to market are critical. AWS enables rapid prototyping, deployment, and scaling without upfront infrastructure costs.
- Startups can launch MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) in days, not months.
- AWS Activate program provides credits, training, and technical support for early-stage companies.
- Companies like Slack, Dropbox, and Robinhood used AWS to scale quickly during their growth phases.
With pay-as-you-go pricing, startups only pay for what they use — a massive advantage over traditional IT models.
Enterprises Migrate to AWS for Agility and Security
Large enterprises are increasingly moving their legacy systems to AWS to improve agility, reduce costs, and enhance security.
- Companies like Capital One, BMW, and Unilever have completed major cloud migrations on AWS.
- AWS provides tools like AWS Migration Hub and Application Discovery Service to streamline the transition.
- Hybrid cloud solutions allow businesses to maintain on-premises systems while integrating with AWS resources.
According to a 2023 McKinsey report, organizations that migrated to AWS saw an average 40% reduction in IT costs and a 60% improvement in deployment speed.
Security and Compliance in AWS: Built for Trust
Security is not an afterthought in AWS — it’s built into the foundation. AWS operates under a shared responsibility model, where AWS manages the security of the cloud, and customers manage security in the cloud.
Shared Responsibility Model Explained
This model defines who is responsible for what in the cloud environment.
- AWS Responsibilities: Physical security of data centers, hardware, software, networking, and facilities.
- Customer Responsibilities: Managing access controls, encryption, firewall configurations, and application-level security.
- For example, AWS ensures the hypervisor is secure, but the customer must patch the operating system running on their EC2 instance.
Understanding this model is crucial for maintaining a secure cloud environment. AWS Shared Responsibility Model details.
AWS Security Tools and Best Practices
AWS offers a robust suite of security tools to help organizations protect their data and applications.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user access and permissions with fine-grained policies.
- AWS Shield: Protects against DDoS attacks.
- AWS WAF: Web Application Firewall that blocks common web exploits.
- AWS Config: Tracks configuration changes and ensures compliance with organizational policies.
- AWS GuardDuty: Intelligent threat detection using machine learning.
Best practices include enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), encrypting data at rest and in transit, and regularly auditing configurations using AWS Trusted Advisor.
Cost Management and Optimization in AWS
One of the biggest challenges organizations face with AWS is controlling costs. While the pay-as-you-go model is flexible, unmonitored usage can lead to unexpected bills.
Understanding AWS Pricing Models
AWS offers several pricing options to suit different needs:
- On-Demand Instances: Pay for compute capacity by the second or hour with no long-term commitments.
- Reserved Instances: Save up to 75% by committing to usage for 1 or 3 years.
- Spot Instances: Bid on unused EC2 capacity for up to 90% off — ideal for fault-tolerant, flexible workloads.
- Savings Plans: Flexible pricing model that applies to a consistent amount of usage (measured in $/hour) over time.
Choosing the right model depends on workload predictability and budget constraints.
Tools to Monitor and Reduce AWS Spending
AWS provides several tools to help you track and optimize your cloud spend.
- AWS Cost Explorer: Visualize and analyze your spending patterns over time.
- AWS Budgets: Set custom cost and usage budgets with alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
- AWS Trusted Advisor: Offers cost optimization recommendations, such as deleting unused resources or resizing underutilized instances.
- AWS Compute Optimizer: Uses machine learning to recommend optimal EC2 instance types based on actual usage.
Regular audits and rightsizing can lead to significant savings — some companies report reducing their AWS bills by 30–50% after optimization.
Serverless Computing with AWS Lambda
Serverless computing is one of the most transformative trends in cloud technology, and AWS Lambda is at the forefront.
What Is AWS Lambda and How It Works
AWS Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You upload your code, and Lambda automatically runs it in response to events.
- Triggers can include HTTP requests via API Gateway, file uploads to S3, or messages from SQS.
- You only pay for the compute time consumed — there’s no charge when your code isn’t running.
- Lambda supports multiple languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, and Go.
Lambda functions are stateless and ephemeral, making them ideal for microservices, real-time data processing, and automation tasks.
Use Cases and Benefits of Serverless Architecture
Serverless doesn’t mean no servers — it means you don’t manage them. This shift brings major benefits:
- Reduced Operational Overhead: No need to patch, monitor, or scale servers.
- Auto-Scaling: Lambda scales automatically from a few requests to thousands per second.
- Faster Time to Market: Developers can focus on writing code, not infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for execution time, down to the nearest millisecond.
Companies use Lambda for image resizing, log processing, chatbots, and backend APIs. For example, Coca-Cola uses AWS Lambda to power its Freestyle soda machines’ cloud connectivity.
AWS Machine Learning and AI Services
AWS is a leader in democratizing artificial intelligence and machine learning, offering tools that make AI accessible even to non-experts.
Amazon SageMaker: Build, Train, and Deploy ML Models
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that enables developers and data scientists to build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale.
- Provides built-in algorithms and Jupyter notebooks for experimentation.
- Automates model tuning with hyperparameter optimization.
- Supports deployment to real-time endpoints or batch processing.
SageMaker removes much of the complexity traditionally associated with ML workflows, allowing teams to go from idea to production faster. Learn more about Amazon SageMaker.
Pre-Built AI Services: Rekognition, Polly, and Comprehend
For organizations that don’t want to build custom models, AWS offers pre-trained AI services:
- Amazon Rekognition: Image and video analysis for facial recognition, object detection, and content moderation.
- Amazon Polly: Text-to-speech service that sounds natural and lifelike.
- Amazon Comprehend: Natural language processing (NLP) to extract insights from text, such as sentiment analysis and entity recognition.
These services are used in applications like customer service chatbots, accessibility tools, and social media monitoring.
Getting Certified in AWS: A Career Game-Changer
AWS certifications are among the most valued credentials in the IT industry. They validate your expertise and can significantly boost your career.
Popular AWS Certifications and Their Value
AWS offers a tiered certification path:
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner: Entry-level, ideal for non-technical roles or beginners.
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate: Focuses on designing distributed systems on AWS.
- AWS Certified Developer – Associate: For developers building and deploying cloud applications.
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer – Professional: For advanced automation and CI/CD pipeline management.
- AWS Certified Machine Learning – Specialty: For AI/ML professionals.
According to Global Knowledge’s 2023 IT Skills and Salary Report, AWS-certified professionals earn up to 25% more than their non-certified peers.
How to Prepare for AWS Certification Exams
Success requires a mix of hands-on experience, study, and practice.
- Use the AWS Training and Certification portal for official courses.
- Practice in the AWS Free Tier — build real projects like a static website or serverless API.
- Take practice exams from providers like A Cloud Guru or Whizlabs.
- Join AWS communities on Reddit, Discord, or LinkedIn for tips and support.
Most experts recommend at least 6 months of hands-on AWS experience before attempting associate-level exams.
The Future of AWS: Trends and Innovations to Watch
AWS continues to innovate at a rapid pace, shaping the future of cloud computing, edge computing, and quantum computing.
AWS Outposts: Bridging Cloud and On-Premises
AWS Outposts brings native AWS services, infrastructure, and APIs into on-premises data centers.
- Enables hybrid architectures for low-latency workloads or data residency requirements.
- Managed by AWS, ensuring consistency with the cloud environment.
- Used in industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing where data must stay local.
Outposts is a strategic move to capture markets where full cloud migration isn’t feasible.
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB) and Blockchain
QLDB is a fully managed ledger database that provides a transparent, immutable, and cryptographically verifiable transaction log.
- Ideal for supply chain, financial systems, and audit trails.
- Unlike blockchain, QLDB is centralized and easier to manage.
- Offers high performance and ACID compliance.
While not blockchain, QLDB brings similar trust benefits with simpler operations.
AWS and the Rise of Edge Computing with Wavelength and Snow Family
As IoT and 5G grow, edge computing is becoming critical. AWS addresses this with:
- AWS Wavelength: Embeds AWS compute and storage services within 5G networks for ultra-low latency.
- AWS Snow Family: Physical devices (Snowcone, Snowball, Snowmobile) for data transfer and edge computing in remote locations.
These services enable real-time processing in environments where connecting to the cloud isn’t practical — like oil rigs, ships, or disaster zones.
What is AWS and why is it important?
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is the world’s leading cloud computing platform, offering over 200 services for computing, storage, databases, machine learning, and more. It’s important because it enables businesses to innovate faster, scale efficiently, and reduce IT costs by leveraging on-demand cloud resources.
What are the most popular AWS services?
The most popular AWS services include Amazon EC2 (compute), Amazon S3 (storage), Amazon RDS (databases), AWS Lambda (serverless), and Amazon CloudFront (content delivery). These form the backbone of most cloud architectures.
How much does AWS cost?
AWS uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model, so costs depend on usage. You can start for free with the AWS Free Tier, which includes limited usage of many services for 12 months. For larger workloads, costs can range from a few dollars to thousands per month based on resource consumption.
Is AWS safe and secure?
Yes, AWS is highly secure. It uses industry-leading encryption, compliance certifications, and a shared responsibility model. AWS manages security of the cloud infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and access controls.
How can I get AWS certified?
You can get AWS certified by choosing a certification path (e.g., Cloud Practitioner, Solutions Architect), studying the official AWS training materials, gaining hands-on experience, and passing the exam. Exams are administered through Pearson VUE and cost between $100 and $300 depending on the level.
AWS has redefined how technology is built, deployed, and scaled in the modern world. From startups to global enterprises, its services empower innovation, reduce costs, and accelerate digital transformation. Whether you’re exploring cloud computing for the first time or looking to deepen your expertise, mastering AWS is a strategic advantage. With continuous innovation in AI, serverless, edge computing, and security, AWS remains at the forefront of the tech revolution — and your journey to mastering it starts now.
Further Reading: