AWS Beanstalk: 7 Powerful Reasons to Use This Game-Changing Tool
Looking for a hassle-free way to deploy your apps in the cloud? AWS Beanstalk might be the ultimate solution you’ve been searching for. It simplifies deployment so you can focus on code, not infrastructure.
What Is AWS Beanstalk and Why It Matters

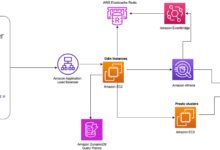
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, commonly known as AWS Beanstalk, is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows developers to quickly deploy and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It automatically handles capacity provisioning, load balancing, scaling, and application health monitoring, making it ideal for developers who want to focus on writing code rather than managing servers.
Core Concept Behind AWS Beanstalk
AWS Beanstalk abstracts the complexity of infrastructure management by providing a layer on top of AWS services like EC2, S3, RDS, and Auto Scaling. When you upload your application code, Beanstalk automatically deploys it using the best practices defined by AWS. This means you don’t need to manually configure EC2 instances, set up load balancers, or manage scaling policies—Beanstalk does it all for you.
- Supports multiple programming languages including Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, and Go.
- Integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like CloudWatch, RDS, and S3.
- Allows full control over the underlying AWS resources if needed.
“Elastic Beanstalk enables you to focus on your application code and lets AWS handle the deployment details.” — AWS Official Documentation
How AWS Beanstalk Differs from Traditional Deployment
Traditional deployment methods require developers to manually configure servers, install dependencies, manage firewalls, and set up monitoring tools. This process is time-consuming and error-prone. In contrast, AWS Beanstalk automates these tasks, reducing deployment time from hours to minutes.
- No need to manually install web servers like Apache or Nginx.
- Automatic OS patching and runtime updates.
- Zero-downtime deployments with rolling updates and blue-green deployment options.
This abstraction allows development teams to move faster, reduce operational overhead, and improve application reliability.
Key Features That Make AWS Beanstalk Stand Out
AWS Beanstalk isn’t just another deployment tool—it’s packed with features designed to streamline the entire application lifecycle. From automatic scaling to integrated monitoring, it’s built to support modern DevOps practices.
Automatic Scaling and Load Balancing
One of the most powerful features of AWS Beanstalk is its ability to automatically scale your application based on traffic. You can define scaling policies based on CPU usage, network traffic, or custom CloudWatch metrics. Beanstalk uses Auto Scaling groups and Elastic Load Balancers to distribute traffic evenly across instances.
- Horizontal scaling: Adds or removes EC2 instances based on demand.
- Vertical scaling: Can be configured with instance type changes during peak loads.
- Supports both Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Classic Load Balancer (CLB).
For example, during a product launch or marketing campaign, your app might experience a sudden spike in traffic. AWS Beanstalk automatically spins up new instances to handle the load and shuts them down when traffic decreases, optimizing cost and performance.
Integrated Monitoring and Health Checks
Beanstalk integrates with Amazon CloudWatch to provide real-time monitoring of your application’s health. It tracks key metrics such as CPU utilization, request count, latency, and error rates. You can set up alarms to notify you when thresholds are breached.
- Environment health dashboard shows status (Green, Yellow, Red).
- Detailed logs can be streamed or downloaded for debugging.
- Custom health checks can be configured for specific endpoints.
This proactive monitoring helps detect issues before they impact users, ensuring high availability and reliability.
How AWS Beanstalk Works Under the Hood
To truly appreciate AWS Beanstalk, it’s important to understand the architecture and components that power it. While it hides complexity, knowing what happens behind the scenes helps in troubleshooting and optimization.
Environment Types in AWS Beanstalk
AWS Beanstalk supports two main environment types: Web Server environments and Worker environments.
- Web Server Environment: Handles HTTP/S requests. Ideal for web applications and APIs.
- Worker Environment: Processes background jobs using Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service). Perfect for tasks like image processing, email sending, or data transformation.
You can even combine both environments in a single application for full-stack processing.
Deployment Mechanisms and Strategies
AWS Beanstalk supports several deployment strategies to minimize downtime and risk:
- All at Once: Deploys the new version to all instances simultaneously. Fast but risky.
- Rolling: Updates instances in batches, reducing impact if something goes wrong.
- Rolling with Additional Batch: Adds extra capacity during deployment to maintain performance.
- Immutable: Creates a new set of instances with the new version and swaps them in after testing.
- Blue/Green: Uses Elastic Load Balancing to switch traffic between old and new environments with zero downtime.
These strategies give you flexibility depending on your application’s criticality and uptime requirements.
Supported Platforms and Languages in AWS Beanstalk
AWS Beanstalk supports a wide range of programming languages and platforms, making it a versatile choice for development teams using different tech stacks.
Officially Supported Runtimes
Amazon maintains official support for the following platforms:
- Java (Tomcat, Corretto)
- .NET on Windows Server
- PHP (Apache)
- Node.js
- Python (WSGI)
- Ruby (Passenger)
- Go
- Docker (single container or multi-container with ECS)
Each platform comes with preconfigured environments, so you don’t have to worry about setting up the runtime manually.
Custom Platforms and Docker Support
If your application uses a language or framework not officially supported, you can create a custom platform using Packer and EC2 Image Builder. Alternatively, you can use Docker to package your application and deploy it as a container.
- Docker allows you to run any language or framework in a containerized environment.
- Multi-container Docker environments use Amazon ECS under the hood.
- You can customize the base image and add your own dependencies.
This flexibility makes AWS Beanstalk suitable for both standard and niche use cases.
Integrating AWS Beanstalk with Other AWS Services
AWS Beanstalk doesn’t exist in isolation—it’s designed to work seamlessly with other AWS services to provide a complete application ecosystem.
Database Integration with Amazon RDS
Beanstalk can automatically provision and manage Amazon RDS instances for your application. During environment creation, you can choose to launch an RDS database (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, or SQL Server) that’s linked to your environment.
- Database credentials are injected into the environment via environment variables.
- Backups, snapshots, and maintenance are handled by RDS.
- You can scale the database independently of the application tier.
This tight integration simplifies database management and ensures secure, reliable data storage.
Storage and File Sharing with S3 and EFS
While EC2 instances in Beanstalk are ephemeral, you often need persistent storage. AWS provides two main solutions:
- Amazon S3: Ideal for storing static assets like images, videos, and logs. Beanstalk can be configured to upload logs to S3 automatically.
- Amazon EFS (Elastic File System): Provides a shared file system that can be mounted across multiple EC2 instances. Useful for applications that require shared storage, like content management systems.
By integrating S3 and EFS, you can build scalable, fault-tolerant applications that don’t lose data during instance replacement.
Best Practices for Using AWS Beanstalk Effectively
To get the most out of AWS Beanstalk, it’s essential to follow best practices that enhance performance, security, and maintainability.
Use Configuration Files (ebextensions)
Beanstalk supports .ebextensions—a directory in your application source bundle that contains configuration files written in YAML or JSON. These files allow you to customize the environment without modifying the code.
- Install additional software (e.g., ImageMagick, FFmpeg).
- Modify configuration files (e.g., nginx.conf, httpd.conf).
- Run scripts during deployment.
Example: You can use .ebextensions to install a Node.js package globally or configure SSL settings.
Enable Managed Platform Updates
AWS regularly updates the underlying platform with security patches and performance improvements. You can enable managed updates to automatically apply these changes during a maintenance window.
- Reduces security vulnerabilities.
- Ensures compatibility with the latest AWS features.
- Can be scheduled during off-peak hours to minimize disruption.
This feature is especially valuable for maintaining compliance and reducing manual maintenance tasks.
Common Use Cases and Real-World Applications of AWS Beanstalk
AWS Beanstalk is used by startups, enterprises, and government agencies to deploy a wide variety of applications. Understanding real-world use cases helps illustrate its versatility.
Startup MVP Development
Startups often need to launch a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) quickly with limited resources. AWS Beanstalk allows them to deploy a web application in minutes without hiring a DevOps team.
- Fast time-to-market.
- Low operational overhead.
- Cost-effective scaling as user base grows.
Many successful startups have used Beanstalk as their initial deployment platform before moving to more complex architectures.
Enterprise Application Modernization
Large organizations are modernizing legacy applications by migrating them to the cloud. AWS Beanstalk provides a smooth transition path for applications built on Java, .NET, or PHP.
- Reduces dependency on on-premises servers.
- Improves scalability and disaster recovery.
- Integrates with existing IAM and VPC configurations.
For example, a financial institution might migrate its customer portal to Beanstalk to improve uptime and security.
Limitations and When Not to Use AWS Beanstalk
While AWS Beanstalk is powerful, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding its limitations helps you make informed decisions.
Less Control Compared to EC2 or ECS
Beanstalk abstracts infrastructure, which is great for simplicity but can be limiting for advanced use cases. If you need fine-grained control over networking, security groups, or container orchestration, services like Amazon ECS or EKS might be better choices.
- Custom kernel tuning is not possible.
- Some AWS features require manual intervention via EC2.
- Debugging can be harder due to abstraction.
For highly regulated environments or performance-critical applications, direct infrastructure management may be necessary.
Not Ideal for Microservices at Scale
While Beanstalk can run microservices, it’s not designed for large-scale microservices architectures. Each environment runs a single application, so managing dozens of microservices becomes cumbersome.
- Limited support for service discovery.
- No built-in API gateway integration.
- Higher operational overhead when managing multiple environments.
In such cases, Kubernetes (EKS) or serverless architectures (Lambda + API Gateway) are more suitable.
Getting Started with AWS Beanstalk: A Step-by-Step Guide
Ready to deploy your first application? Here’s a quick guide to get you started with AWS Beanstalk.
Create an Application and Environment
1. Log in to the AWS Management Console.
2. Navigate to the Elastic Beanstalk service.
3. Click “Create Application.”
4. Enter a name and description.
5. Choose a platform (e.g., Node.js).
6. Upload your code (ZIP file or connect to CodeCommit/GitHub).
7. Click “Create.”
AWS will provision the environment and deploy your app. You’ll get a URL like myapp.us-east-1.elasticbeanstalk.com.
Deploy Updates and Manage Environments
Once your environment is running, you can:
- Deploy new versions via the console, CLI, or CI/CD pipeline.
- Clone environments for testing.
- Swap URLs between environments for blue-green deployments.
- Monitor logs and metrics in real time.
You can also use the AWS CLI or SDKs to automate deployments, making it easy to integrate with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Bitbucket Pipelines.
What is AWS Beanstalk used for?
AWS Beanstalk is used to deploy and manage web applications and services in the cloud without dealing with infrastructure. It automates deployment, scaling, and monitoring, supporting languages like Java, Python, Node.js, and more.
Is AWS Beanstalk free to use?
AWS Beanstalk itself is free, but you pay for the underlying AWS resources (EC2, S3, RDS, etc.) used by your application. There are no additional charges for using Beanstalk.
How does AWS Beanstalk differ from AWS Lambda?
Beanstalk runs full applications on servers (or containers), while Lambda runs code in a serverless, event-driven model. Beanstalk is better for long-running apps; Lambda is ideal for short, event-based tasks.
Can I use Docker with AWS Beanstalk?
Yes, AWS Beanstalk supports both single-container and multi-container Docker environments. You can deploy custom Docker images and define complex application architectures.
Does AWS Beanstalk support CI/CD?
Yes, Beanstalk integrates with AWS CodePipeline, CodeBuild, and third-party tools like Jenkins and GitHub Actions to enable continuous integration and deployment workflows.
AWS Beanstalk is a powerful, developer-friendly service that simplifies cloud deployment without sacrificing control. Whether you’re launching a startup MVP or modernizing enterprise applications, Beanstalk offers the right balance of automation and flexibility. While it may not suit every use case—especially large-scale microservices—it remains a top choice for teams looking to deploy applications quickly and reliably. By leveraging its features like auto-scaling, health monitoring, and seamless AWS integration, you can focus on what matters most: building great software. Explore the official AWS Beanstalk documentation to dive deeper and start your journey today.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: